- 7shares
- 2Facebook
- 5LinkedIn
- 0Pinterest
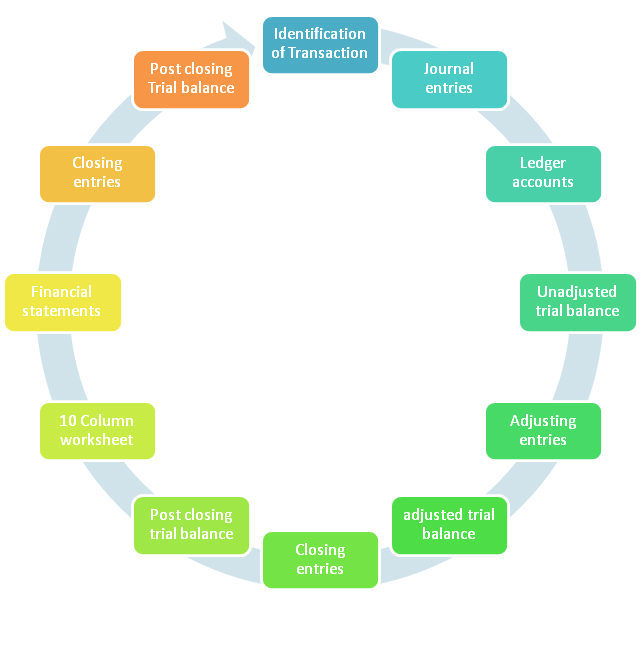
Accounting cycle Definition:
Accounting cycle is the collective process of recording and processing accounting transactions. It stars from occurrence of transaction and ends on after closing trial balance.
Accounting cycle steps:
Following are steps of accounting cycle.
- Trasaction:
- Journal entries
- Posting
- Unadjusted trial balance
- Adjusting entries
- Adjusted trial balance
- Preparation of finanacial statements
- Closing entries
- Post closing trial balance
Accounting cycle Flowchart:
Explanation of each step:
Analysing transaction and recording in books:
First step in accounting cycle is identify, analyse and record the transaction. Easy way to understand the transaction is identify the accounts involved and determine whether it is personal or business trasaction. In small business, many transactions are for personal purpose. Do not record those transaction in books but show them in capital account of owner. This is the duty of junior accountant generally.
Journalizing the transaction:
Next step is do journal entry of transaction. Journal entry can be done using accounting equation or golden rules of accounting. Remember that right entry leads to right accounting and helps to show right profit/loss for the business and true position of assets and liablities.
Posting to the ledger:
There are plenty of transactions in business. These transactions are segmented in ledgers ( Account). All the transactions related to same account is recorded in ledger. Ledger posting is easy process. In which, debit entry is posted on debit side of ledger and credit entry is posted on credit side of ledger. After posting, Balancing is done by finding difference of sum of debits and sum of credits. Read full article about preparation of T accounts- Here.
Preparation of unadjusted trial balance:
All the balances of ledgers are posted in unadjusted trial balance. Unadjusted trial balance is list of accounts and balances without adjustments. Learn how to prepare unadjusted trial balance from this post.
Adjusting entries:
There are many adjustments which may be pending to be recorded or considered in accounts. Those transactions are recorded using adjusting entries. Adjusting entries are ledger entries done to record adjustments in accounts.
Following adjustments are covered under adjustments:
- Prepayments and accruals
- Writing off depreciation
- Writing off bad debt
- Adjusting entry for obsolesce inventory.
- Recording ommitted transactions – Unrecorded bills or invoices
Preparation of adjusted trial balance:
Once all the adjustments are recorded through adjusting entries, adjusted trial balance is prepared considering adjustments.
Preparation of 10 column worksheet:
In large companies, accountant prepare 10 column worksheet to track all the remaining adjustments. In 10 column worksheet, there are 10 columns covering unadjusted trial balance, adjustments, income statements and balance sheet. Preparation of 10 column worksheet makes preparation of financial statements easy and error free. Remember that it is not compulsory to prepare 10 column worksheet in accounting.
Preparation of financial statements:
Financial statements include income statement ( Profit and loss account) and Balance sheet and cash flow statements as part of financial statements.
Income statement:
Income statement which is also called profit and loss account ( P&L account) . Income statement is In income statements, all the incomes are recorded on credit side and all the expenses are recorded on debit side. Profit / Loss is calculated using the difference of sum of both side.
Balance sheet:
Balance sheet presents financial position of company for reporting date. Balance sheet covers three elements refers as Assets, Liabilities and capital.
Notes to Financial statements:
Financial statements also includes notes to financial statements.Common notes includes advice on significant accounting policies, notes about depreciating assets, notes about inventory valuation, notes about disclosure of subsequent events, notes about contingent liabilities, notes about dept, consolidation financial statements notes.
Closing entries:
Closing entries are required to close all the temporary accounts ( Income accounts, Expense accounts and withdrawals) and transfer their balances to permanent account ( Income statements). In this way, all the income and expense has nil balance at the end of accounting period and next year, the income accounts and expense accounts are started with zero. Closing of books needs time and effort when there are large number of ledgers and sub ledgers or there are many subsidiaries.
Post closing trial balance:
Post closing trial balance is prepared after closing entries are done. It contains all the balance sheet accounts.It helps to verify that sum of the debit balances are equal to the sum of the credit balances. It is last step in accounting cycle.
Accounting cycle Example:
We understand accounting cycle with following transactions of business.
- Mr. Zen has started business of selling furniture on 1/5/2015 with $2,00,000 capital.
- Mr. Zen has bought furniture ( Inventory) on cash $2,0000.
- Mr. Zen has purchased van for business use – $2000.
- Mr. Zen has received loan from bank $10,000.
- Mr. Zen has sold furniture for $30,000 on cash.
- Mr. Zen has sold furniture for $2,000 on 30 days credit to Mr. Smart.
- Mr. Zen has paid salary to Miss Lilly $500.
- Mr. Zen has purchase furniture on credit $1,000 from Mr.Happy .
- Mr. Zen has sold furniture on cash $1600.
- Mr. Zen has received money from Mr. Smart.
- Mr. Zen has paid advertising expense $200.
- Mr.Zen has withdraws $300 from business for personal use.
- Mr. Zen has paid $200 as taxes.
- Received purchase order $2000.
Accounting cycle steps for above example:
Analysing transactions and recording in books:
First step is identifying and analyzing relevant transaction. Some transactions are relevant to personal account of Mr.zen which we transfer to capital account. In transaction no. 14, there is order received. Order received is not monetary transaction so we ignore that transaction while making accounts.
Journal entry of transaction:
From above transaction, we make journal entries.
| No. | Entry | Dr | Cr |
| 1 | Bank a/c Dr | 2,00,000 | |
| To Mr. Zen a/c | 2,00,000 | ||
| 2 | Purchase a/c Dr | 20,000 | |
| To Bank | 20,000 | ||
| 3 | Van a/c Dr | 2,000 | |
| To bank | 2,000 | ||
| 4 | Bank a/c Dr | 10,000 | |
| To Loan a/c | 10,000 | ||
| 5 | Bank a/c Dr | 30,000 | |
| To Sales a/c | 30,000 | ||
| 6 | Mr. Smart a/c Dr | 2,000 | |
| To Sales a/c | 2,000 | ||
| 7 | Salary a/c Dr | 500 | |
| To bank | 500 | ||
| 8 | Purchase a/c Dr | 1,000 | |
| To Mr. Happy | 1,000 |
For remaining transaction, do journal entry your own as exercise.
Preparation of Ledgers:
From journal entries, we prepare ledgers. If you are not familiar with process of preparation of T accounts, read my post here. I have already prepared the ledgers which you can see below:
Bank a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ | |
| To Mr.Zen | 2,00,000 | By salary | 500 | |||
| To Loan | 10,000 | By purchase | 20,000 | |||
| To sales | 30,000 | By advertising | 200 | |||
| To sales | 1,600 | By Drawing | 300 | |||
| To Mr. Smart | 2,000 | By Tax | 200 | |||
| By van | 2,000 | |||||
| By Balance c/d | 2,20,400 | |||||
| 2,43,600 | 2,43,600 | |||||
Zen a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ |
| To Bal c/d | 2,00,000 | By bank a/c | 2,00,000 | ||
| 2,00,000 | 2,00,000 |
Purchase a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ |
| To Bank a/c | 20,000 | By balance c/d | 21,000 | ||
| To Mr. Happy | 1,000 | ||||
| 21,000 | 21,000 |
Van a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ |
| To bank | 2,000 | By balance c/d | 2,000 | ||
| 2,000 | 2,000 |
Sales a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ |
| To bal. c/d | 33,600 | By Bank a/c | 30,000 | ||
| By Mr. Smart a/c | 2,000 | ||||
| By bank a/c | 1600 | ||||
| 33,600 | 33,600 |
Mr.smart’s a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ | |
| To Sales | 2,000 | By bank a/c | 2,000 | |||
| 2,000 | 2,000 | |||||
Salary a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ |
| To Bank | 500 | By bal c/d | 500 | ||
| 500 | 500 |
Mr. Happy a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ |
| To bal. c/d | 1,000 | By Purchase | 1,000 | ||
| 1,000 | 1,000 |
Advertising Exp
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ |
| To Bank | 200 | By bal c/d | 200 | ||
| 200 | 200 |
Drawing a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ |
| To bank | 300 | By bal c/d | 300 | ||
| 300 | 300 | ||||
Tax a/c
| Date | Part. | $ | Date | Part. | $ |
| To Bank | 200 | By bal c/d | 200 | ||
| 200 | 200 |
Preparation of Unadjusted Trial Balance:
From balances of ledgers above, we prepare unadjusted Trial balance.
| Ledger | Debit | Credit |
| Bank | 2,20,400 | |
| Zen | 2,00,000 | |
| Tax | 200 | |
| Drawing | 300 | |
| Advertising | 200 | |
| Mr.Happy | 1,000 | |
| Salary | 500 | |
| Loan from Bank | 10,000 | |
| Sales | 33,600 | |
| Purchase | 21,000 | |
| Van | 2,000 | |
| Total | 2,44,600 | 2,44,600 |
Recording adjustments:
Following adjustments are needed to record:
- Salary $100 is pending at year end.
- Advance received from customer $200.
- Loan repaid $200 which is pending to record.
- Insurance paid in advance $400.
We make following adjusting entries:
| No. | Journal Entry | Debit | Credit |
| 1 | Salary a/c Dr | 100 | |
| To salary Payable a/c | 100 | ||
| 2 | Bank a/c Dr | 200 | |
| To Advance received | 200 | ||
| 3 | Loan from bank a/c Dr | 200 | |
| To Bank | 200 | ||
| 4 | Insurance paid in advance Dr | 400 | |
| To bank a/c | 400 |
Preparation of adjusted Trial balance :
Adjusted trial balance has same format as of unadjusted trial balance. The difference is that it considered adjustment made at year end.
| Ledger | Debit | Credit |
| Bank | 2,20,000 | |
| Zen | 2,00,000 | |
| Tax | 200 | |
| Drawing | 300 | |
| Advertising | 200 | |
| Mr.Happy | 1,000 | |
| Salary | 600 | |
| Loan from Bank | 9,800 | |
| Sales | 33,600 | |
| Purchase | 21,000 | |
| Van | 2,000 | |
| Insurance paid in advance | 400 | |
| Advance Received | 200 | |
| Salary payable | 100 | |
| Total | 244700 | 2,44,700 |
Preparation of 10 column worksheet:
10 column worksheet consist of unadjusted trial balance balances, adjustment, adjusted trial balance’ figures, Income statements, balance sheet. We discuss preparation of 10 column worksheet in upcoming article. Remember that preparation of 10 column worksheet is not mandatory and worksheet is not part of financial statements.
Preparation of financial statements:
Financial statements consist income summary account or profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Income summary account
| Expense | $ | Income | $ |
| Advertising | 200 | Sales | 33600 |
| Salary | 600 | ||
| Purchase | 21000 | ||
| Tax | 200 | ||
| Net Profit | 11,600 | ||
| 33,600 | 33,600 |
Balance Sheet
| Asset | $ | Liabilities | $ |
| Van | 2000 | Capital | 2,11,300 |
| Bank | 2,20,000 | Loan From bank | 9,800 |
| Insurance paid in advance | 400 | Mr.Happy | 1,000 |
| Advance received | 200 | ||
| Salary Payable | 100 | ||
| 2,22,400 | 2,22,400 |
Closing entries:
Closing entries is process of transfer temporary accounts to permanent account. It is last step in accounting cycle.
| Entry | Dr | Cr |
| Profit and loss account Dr | 22,000 | |
| To Advertising a/c | 200 | |
| To salary a/c | 600 | |
| To Tax | 200 | |
| To Purchase a/c | 21000 | |
| Sales a/c Dr | 33,600 | |
| To Profit and loss a/c | 33,600 | |
| Profit and loss a/c Dr | 11,600 | |
| To Zen a/c | 11.600 |
Post closing trial balance:
Post closing trial balance is snapshot of balance sheet presented in trial balance format.
| Ledger | Debit | Credit |
| Van | 2,000 | |
| Bank | 2,20,000 | |
| Insurance paid in advance | 400 | |
| Loan from bank | 9,800 | |
| Mr.Happy | 1,000 | |
| Advance received | 200 | |
| Salary payable | 100 | |
| Mr.Zen | 2,11,300 | |
| 2,22,400 | 2,22,400 |
In this article, you learn complete accounting cycle from preparation of ledgers to closing entries. If you want to test your accounting knowledge, you can join my accounting video course.
- 7shares
- 2Facebook
- 5LinkedIn
- 0Pinterest
